
10 Most Common WordPress Security Issues and How to Fix Them
Ranging from local start-ups to global enterprises, WordPress has become the backbone for many websites. Today, it powers 43.4% of all websites as their CMS.
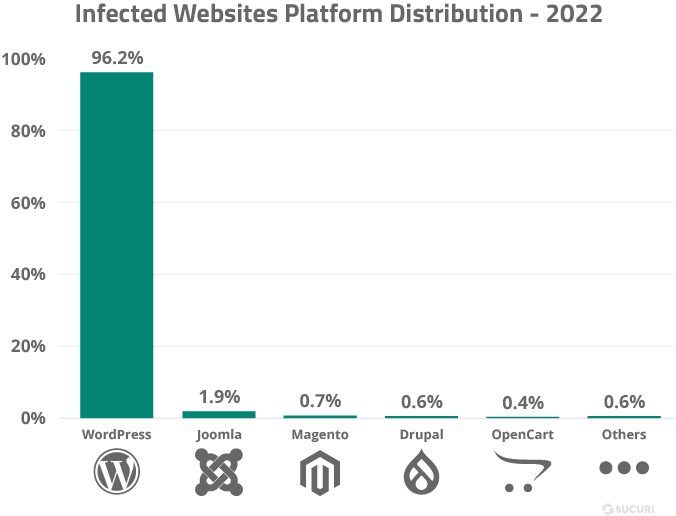
Unfortunately, its high popularity is what makes it one of the most common targets for hackers. No wonder, WordPress itself faces about 90,000 attacks per minute! As per Sucuri’s annual hacked website report in 2022, WordPress has been accountable for 96.2% of infections.
So, even with the tiniest security bolt being left loose, the consequence can be severe as digital threats lurk around each and every corner of the internet. That is why ensuring the security of WordPress is a must. However, whilst the damage has already been done, there is still hope. There are bunch of ways to recover content, repair the harm and protect your site.
In this article, we will discuss the most common WordPress website security issues that you should know about, as well as the steps you can take to prevent those threats.
1. Weak passwords
Weak passwords are one of the most significant security vulnerabilities for WordPress websites. However, site owners and users often go for an easy-to-guess, short, and simple password, and this is what makes it easier for hackers to access a website. When users reuse passwords across multiple sites, attackers can easily use the stolen credentials to access other ones if one site gets compromised.
How to fix it?
It is wiser to go for a strong password that can be at least 12 characters long with a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers and other special characters. Try to avoid common words, names, birthdays or addresses in your password and try to put unique passwords for different accounts.
You can use password managers such as Bitwarden, 1Password or LastPass to store and generate strong, unique passwords for all your accounts so that you can easily manage and remember complex passwords.
2. Search Engine Optimisation spam
SEO spam, also known as search engine poisoning, often leads to the site being backlisted by search engines for keyword stuffing, spammy backlinks, hidden texts and links or phishing pages. Hackers target top-ranking pages in search results to infect them.
The hackers simply insert keywords here and there into relevant pages while keeping your code relatively intact. That is why SEO spam is considered very dangerous, as it is very difficult to detect and is mostly noticeable to SEO crawlers.
How to fix it?
Use security plugins such as Wordfence, Sucuri and All In One WP Security and Firewall to scan your site regularly for SEO spam. Always check your website’s content and backlinks manually to make sure no unauthorised changes have been made. You can set up Google Search Console to alert you to potential SEO spam issues.
3. Outdated plugins, WordPress core and themes
If you are one of the WordPress users using the outdated software version, there is a high chance that your site is at significant risk. From WordPress core to themes to plugins, each of these components requires regular updates to fix bugs, patch security vulnerabilities and introduce new features. However, when the updates are not applied, the components become outdated.
Suppose when you are running an outdated version, your site will be exposed to known vulnerabilities. Also, there will be miss out on new features and improvements alongside the rise of compatibility issue, resulting in a poor user experience, dysfunctional features or site crash. Note that, older version of themes and plugins are considered more susceptible to malware infections.
How to fix it?
Check for updates to the WordPress core, themes and plugins regularly. To monitor update notifications, you can enable email notifications or pay attention to update alerts in your WordPress dashboard. Every time you see updates available, you either install them manually or use a plugin to install them automatically anytime you go live.
But make sure the automatic updates are enabled only for trusted sources. Remember to back up your site before applying updates so that you can restore your site to its previous state if any update issues occur.
4. Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is used by hackers to infect any site with malicious code in order to steal sensitive information. Malware can be of various types, and some of the common ones affecting WordPress sites are malicious redirects, drive-by downloads and backdoor attacks.
From insure hosting to unverified plugins and themes to phishing and social engineering, there are many ways of how malware infiltrates WordPress site.
How to fix it?
If you don’t want to fall victim to malware, use security plugins to scan regularly. You can install a malware scanner to block malware and potentially unwanted programs. Or just identify and remove infected files. Make sure to choose a reputable hosting provider that comes with strong security measures.
5. Cross-site scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities are often found in WordPress plugins. It allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages and these scripts can execute in the context of the user’s browser, leading to malicious outcomes, such as stealing session cookies, defacing websites, or redirecting users to malicious sites.
How to fix it?
In order to protect against XSS attacks, you must have to keep your site updated at any cost alongside the WordPress themes and plugins. Also try to remove or decode any characters that could be used in a malicious script. Use security plugins to detect and block XSS attacks.
6. SQL injections
SQL is a programming language that is used mostly to get quick access to stored data on a particular site. SQL injection is another common WordPress website security threat that often happen when cybercriminals get unauthorised access to your database and make direct changes to your database.
Poorly coded or unmaintained plugins and themes can lead to SQL injection vulnerabilities. Also, improperly sanitised user inputs can be manipulated to include SQL commands.
How to fix it?
You must implement restrictions and limitations on your form submission. Also, use prepared statements and parameterised queries to ensure that SQL code and user input are separated. This will prevent attackers to manipulate the query. Keep WordPress themes and plugins updated while employing security plugins to scan for SQL injection vulnerabilities.
7. DDoS Attack
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack in WordPress is basically a malicious attempt that disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service or network. It eventually floods a site’s server with loads of questions which ends us consuming all the resources of the site.
Just imagine, your site getting hundreds of requests per second, coming in from thousands of bots from all over the world. As a result, it becomes sluggish to the point of crashing.
How to fix it?
You can take specialised DDoS protection services or solutions provided by third-party vendors to detect and mitigate DDoS attacks at the right time. Also, monitor incoming traffic patterns to detect sudden spikes or unusual patterns and implement an automated system to trigger alerts or actions. You can even configure firewalls to filter out malicious traffic depending on predefined rules.
8. Brute Force Attack
A brute force attack occurs when hackers use trial and error by guessing login information and encryption keys to access a website using automated software. On WordPress, these attacks typically target the login page by attempting several combinations of usernames and passwords till the right one is found.
Here attackers often target common usernames like admin or known ones to gather information from other sources or use automated scripts or bots to try thousands of username password combination in a short period.
How to fix it?
You have to ensure all of users are using complex, unique passwords including a mix of letters, numbers and special characters. Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication.
You can event implement captchas on the login page to differentiate between human users and bots. For the best results regularly audit security settings and logs to detect any potential threats early.
9. Hotlinking
Hotlinking happens when someone links directly to images, videos or other media files on your website from their website without permission or credit. Hotlinks can result in bandwidth drain which can slow down your site and increase hosting cost. Also, as your media contents are being used with no permission, it can affect your content’s value and SEO ranking.
How to fix it?
Regularly monitor your site’s bandwidth usage and media access logs to identify and address unauthorised use. Use tools like Google Search Console to check your media files for external links. Another thing you can do is configure your server settings by adding specific rules to block hotlinking.
10. HTTP instead of HTTPS
Using HTTP instead of HTTPS can expose your site to multiple security vulnerabilities. As HTTP does not encrypt the data exchanged between the user’s browser and the web server, it can be easily intercepted by hackers.
Also, there is a chance of man-in-the-middle attacks where attackers can intercept and alter the communication between the user and the server by injecting malicious code or redirecting users to unauthorised websites.
How to fix it?
Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from any reputable certificate authorities to encrypt data exchanged between the browser and the server. Make sure to use HTTPS instead of HTTP on all of your internal links, images and scripts. Also implement 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS to ensure all of your traffic is directed to the secure version of your site.
How to check WordPress vulnerability
Plugins are often considered as the most-used go to solutions, but they are not the only viable method to detect issues. Along with using plugins, there are other ways to scan WordPress for vulnerabilities.

Security plugins
Using plugins to check for WordPress vulnerabilities is highly effective. They are easy to use, provide real-time monitoring and alerts while offering comprehensive reporting. Plugins can be configured to automatic scanning as well.
Many of the plugins even provide several layers of protection into one package. For example, plugins like Wordfence security, Sucuri security or iThemes security offer features such as malware scanning, firewalls and real-time threat detection.
Manual scanning
You can go for manual scanning, especially if you want to tailor your inspection to a particular site configuration. Also, when you scan your site manually, you get a deeper understanding of its structure and components and take immediate action whenever you identify a vulnerability.
Sometimes, automated tools fail to understand the custom codes or specific configurations, whereas manual inspection can provide a secondary layer of verification.
Automatic scanning
Automatic scanning provides round-the-clock protection while detecting and responding to threats in real-time. Anytime a threat is detected, automatic scanners send instant alerts to notify you to take prompt action.
Compared to manual scanning, it is time-saving and ensures consistency. Automated tools also offer features for regular maintenance tasks, such as updating plugins and themes, which are crucial for security.
Online vulnerability scanner
You can use online vulnerability scanners as external tools to get an external perspective on how attackers might view and interact with your site. This will help you identify vulnerabilities that might not be visible from within the server environment.
As it does not require extensive technical knowledge to operate this tool, you can quickly perform scans and receive detailed reports.
How to prevent WordPress website from hacking
As it says, prevention is better than cure, it is wiser to take all the possible security measures before the hacking succeeds and something on your site goes awry. Follow the points below where we summarise the proven ways that can prevent WordPress website from hacking.
- Implement two-factor authentication
- Limit the number of login attempts
- Use a strong password manager
- Regularly update WordPress core, themes and plugins to the latest versions
- Perform regular backups
- Install an SSL certificate
- Disable file editing through the WordPress dashboard
- Scan for malware periodically
- Continuously monitor your site
- Last but not least, choose a reputable WordPress developer
Final words
So, if you want to keep your WordPress site performing at optimal levels, you must familiarise yourself with the most common WordPress security vulnerabilities first and figure out the ways to deal with the possible threats. This will help you take active measures to protect your site from any sort of threats.
You read a lot. We like that
Want to take your online business to the next level? Get the tips and insights that matter.

